Metallurgical Abstracts on Light Metals and Alloys vol.56
The effects of Ag-based fillers' Ti content and elasto-plastic properties on the mechanical behavior of Nb-interlayer inserted Ti-6Al-4V/Si3N4 joint
Fei Shen Ong*, **, Hirobumi Tobe* and Eiichi Sato*
*Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (ISAS/JAXA)
**Department of Materials Engineering, the University of Tokyo
[Published in 13th International Conference on Brazing, High Temperature Brazing and Diffusion Bonding LÖT 2022 (2022) ISBN: 978-3-96144-182-2]
E-mail: sato[at]isas.jaxa.jp
Key Words: brazing, transient-liquid-phase bonding, CTE mismatch, intermetallics
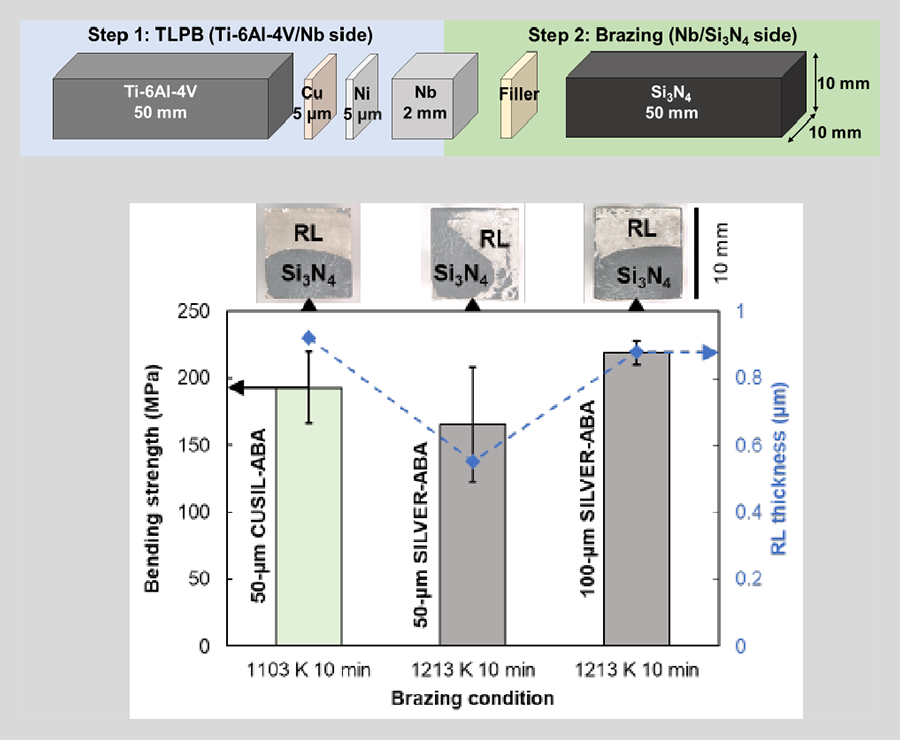
The effects of filler’s Ti content and elasto-plastic properties on the mechanical behavior of Nb-interlayer inserted joints were investigated by brazing with CUSIL-ABA (Ag-35.25Cu-1.75Ti wt.%) and SILVER-ABA (Ag-5Cu-1Al-1.25Ti wt.%) fillers. Prior to brazing the Nb/Si3N4 side, transient-liquid-phase bonding of Ti-6Al-4V/Nb side was conducted with pure Cu and Ni as filler to eliminate brittle intermetallics. Although finite element analysis shows that SILVER-ABA promotes residual-stress relaxation more effectively attributed to its higher plastic deformability, 1.25 wt.% Ti in 50-μm SILVER-ABA is insufficient to promote sound interfacial bonding with ceramics due to thin Ti-Si-N reaction layer and attained lower strength compared to brazing with 50-μm CUSIL-ABA. A countermeasure for strength optimization has been proposed to promote thicker reaction layer on ceramics without increasing the brazing temperature or prolonging holding time to minimize evaporation of Ag under vacuum; brazing with 100-μm SILVER- ABA increases the total Ti content and promotes thicker reaction layer with strength higher than joint brazed with 50-μm CUSIL-ABA.