Metallurgical Abstracts on Light Metals and Alloys vol.56
Relationships between 3D grain structure and local inhomogeneous deformation: A laboratory-based multimodal X-ray tomography investigation
Masakazu Kobayashi*, Yubin Zhang**, Haruki Ishikawa*, Jun Sun***, Jette Oddershede***, Dorte Juul Jensen** and Hiromi Miura*
*Department of Mechanical Engineering, Toyohashi University of Technology, Toyohashi, Aichi 441-8580, Japan
**Department of Mechanical Engineering, Technical University of Denmark, DK- 2800 Kgs. Lyngby, Denmark
***Xnovo Technology ApS, DK-4600 Køge, Denmark
[Published in Acta Materialia 240 (2022) 118357]
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2022.118357
E-mail: m-kobayashi[at]me.tut.ac.jp
Key Words: Local strain, Plastic deformation, Tomography Three-dimensional grain structure, Aluminum alloy, Microstructural feature tracking method
Relationships between the three-dimensional (3D) grain structure and the local strain distribution within individual grains are investigated. Multimodal X-ray tomography, i.e. attenuation tomography (ACT) and diffraction contrast tomography (LabDCT), was applied, for the first time using a laboratory instrument, to non-destructively characterize the grain structure and the local plastic deformation behavior of a fully recrystallized Al-4mass%Cu alloy. The evolution of the internal strain distribution during tensile deformation was measured in-situ by means of a microstructural feature tracking (MFT) method based on ACT. By a correlation analysis of the microstructural parameters of 855 grains, it was investigated if and how the initial crystallographic orientations and sizes of the grains affect the local deformations. In addition, effects of grain boundaries were analyzed. Only weak correlations are found. It is suggested that specific interactions between neighboring grains, which depend on parameters such as grain shapes and orientation differences, are of critical importance for the development of the local strains.
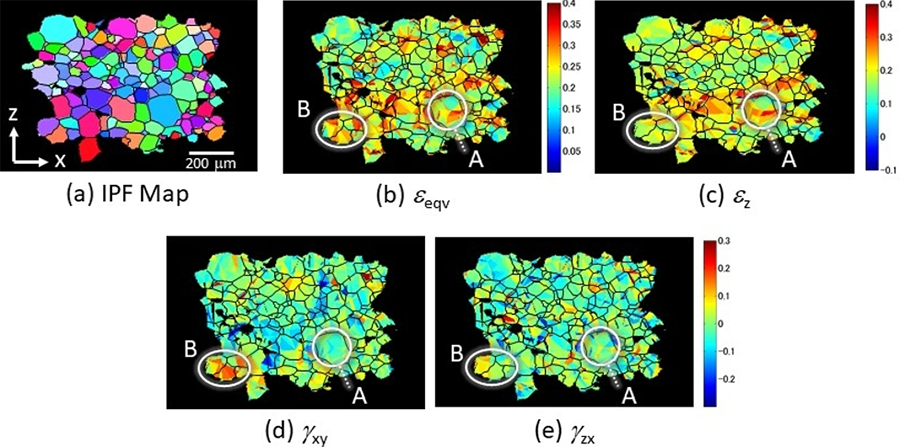
Effect of shear strain components on equivalent strain. (a) orientation map, (b) equivalent strain, (c) strain along the tensile direction, εz , (d) γyx shear strain and (e) γzx shear strain.
