Metallurgical Abstracts on Light Metals and Alloys vol.56
Thermal Stability of L12 Modified Al2.5Cu0.5Ti Particles in Al Matrix
Manasi Shrikrishna Yadav*, Yoshimi Watanabe* and Hisashi Sato*
* Nagoya Institute of Technology
[Published in Physica Status Solidi B, 259, No. 9, 2100603 (6 pages) (2022)]
https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.202100659
E-mail: sato.hisashi[at]nitech.ac.jp
Key Words: Thermal stability, Intermetallic compound, L12-modified Al2.5Cu0.5Ti, Gas atomization, Spark plasma sintering (SPS)
Herein, the thermal stability of two morphologically differently shaped L12-modified Al2.5Cu0.5Ti intermetallic compound particles in the same Al matrix is studied by heating the Al– Al2.5Cu0.5Ti refiner fabricated by spark plasma sintering (SPS). Studying the thermal stability of two morphologically differently shaped L12-modified Al2.5Cu0.5Ti intermetallic compound particles in the same Al matrix allows us to control the external experimental factors for both particles at the same time. This gives better results for comparative studies. The result shows that the heat treatment conditions and the different morphology of the L12-modified Al2.5Cu0.5Ti particles can affect the thermal stability of Al2.5Cu0.5Ti particles in the Al matrix. In addition, the effect of heat treatment on the hardness behavior is evaluated with the Vickers microhardness test. The result shows the variation in hardness with increased heating time.
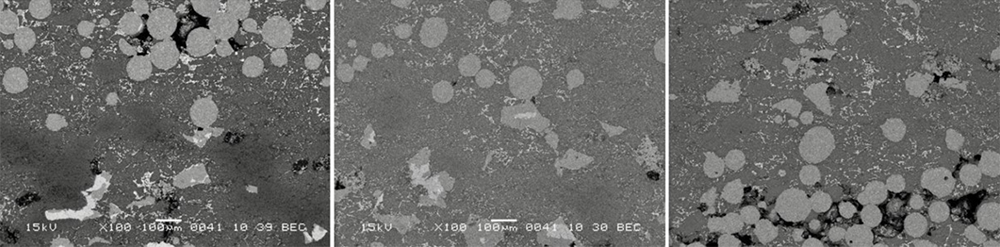
SEM microstructure (BEC) of Al–10vol% (Al2.5Cu0.5Ti) specimen fabricated by SPS and heat treated at 650 ℃ for 3, 5, and 10min, respectively.
